About DMARC
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an open email standard published in 2012 by the industry consortium DMARC.org to protect the email channel. DMARC extends previously established authentication standards for email and is the only way for email senders to tell email receivers that emails they are sending are truly from them.
DMARC allows companies that send email to:
- Authenticate all legitimate email messages and sources for their email-sending domains, including messages sent from your own infrastructure as well as those sent by 3rd parties.
- Publish an explicit policy that instructs mailbox providers what to do with email messages. Policies can instruct that messages that are provably authentic to be directed to an inbox folder. Messages that are provably inauthentic can either be sent to a junk folder or rejected outright, protecting unsuspecting recipients from exposure to attacks.
- Gain intelligence on their email streams by letting them know who is sending mail from their domains. This data helps companies to not only identify threats against their customers, but also discover legitimate senders that they may not even be aware of.
History: The Need for DMARC
Email – despite its importance, ubiquity, and staying power – has never been secure.
Prior attempts at security have failed to solve email’s fundamental flaw – anyone can send email using someone else’s identity. This flaw has put the power of the world’s most admired brands in criminal hands: through email, criminals can use almost any brand to send spam, phishing emails, and malware installs, inflicting direct losses to customers and eroding the brand equity companies have spent years building up.
Many of the most respected brands in the world, including Facebook, Apple, JPMorgan Chase and PayPal, have adopted the DMARC standard to protect their customers and their brand.
Using DMARC, companies gain unprecedented visibility into legitimate and fraudulent mail sent using their domain names. The magic of DMARC is the ability to understand all the different mail streams being sent claiming to be from you - third parties, business units, threat actors. The overall impact to companies that have adopted DMARC is preservation of brand equity, elimination of customer support costs related to email fraud, and renewed trust and engagement in the company’s email channel.
DMARC – an open standard enabled on 70% of the world’s inboxes and also by the most security-forward brands – is the only solution that enables Internet-scale email protection and prevents fraudulent use of legitimate brands for email cyberattacks.
Who Endorses DMARC?
DMARC is endorsed by the world’s largest senders, receivers, and industry consortia. More than 2.5 Billion Mailboxes Worldwide are DMARC-enabled.
Some of the world’s largest email Senders supporting the DMARC standard include the following organizations:

Some of the world’s largest email Receivers supporting DMARC include the following:

In addition, the DMARC standard is endorsed by the following government agencies and industry trade organizations:
Government Agencies
NIST - the National Institute of Standards and Technology
https://www.nist.gov/
FTC - the Federal Trade Commission
https://www.ftc.gov/
GOV.UK - https://www.gov.uk/
Industry Associations
OTA - Online Trust Alliance
https://otalliance.org/
M3AAWG - Messaging Malware Mobile Anti-Abuse Working Group
https://www.m3aawg.org/
DMARC.org - https://dmarc.org/
FS-ISAC - Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center
https://www.fsisac.com/
NH-ISAC - National Health Information Sharing and Analysis
https://nhisac.org/
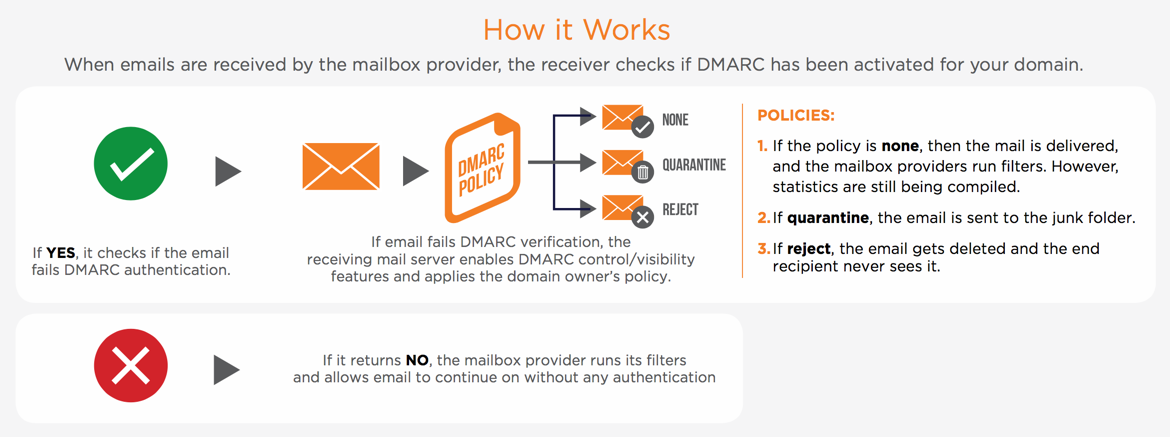
What is DMARC Enforcement?
When you set a DMARC policy for your organization, you as an email sender are indicating that your messages are protected. The policy tells a receiver what to do if one of the authentication methods in DMARC passes or fails.